In git, there can be many branches. Master Branch is the main branch in git. It’s kept safe without breaking. New experiments and testing functionalities are tried out by creating a sub-branch (side branch).
The side branch is the experimental branch derived from the main branch. Experimental code gets committed to the side branch. Once the code is working great then it can be merged to the master branch.
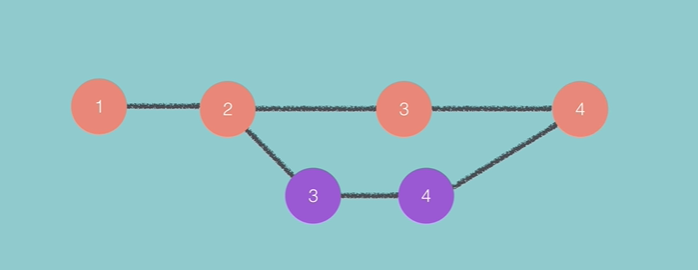
In the above picture 1 – 2 – 3 is the master branch.
3 – 4 is the side branch (experimental code) – its then merged to the master branch once finalised.
git log
This command can be used to find the current branch.
Git command for creating new Branch from Master Branch
git branch name_of_branch
examples of git branches:
git branch develop
git branch feature
git branch hot-fix
git branch QA
git branch smc-feature-login
Git command to Get list of Branches
git branchIt will list all the branches. Also highlight the current active branch.
Git command to checkout to new Branch
git checkout name_of_branch
eg: git checkout develop
After checking out to the new branch, we can make changes to codes and then commit.
Now try, git log to view the changes in branches.
It will list the branches.
How to Merge side branch to Master Branch
In order to merge the sub branch to the master branch, firstly we have to checkout to the master branch.
git checkout master
Then we need to perform the merge command.
git merge name_of_branch
eg: git merge develop
Now a text editor may open in the terminal. Its for the merge message.
We can exit that editor by the following command: :q!
Its done.
Now verify by using git log in the master branch.
Then it can be pushed to the server using:
git push origin master -u
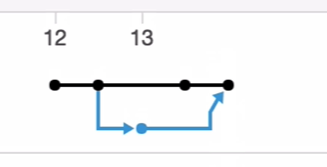
In github website , If we go to Insights -> graph -> network menu of the repository, we can see the graphical representation.