Optimizing the routes code by Chaining multiple routes together. GET, POST, DELETE request routes are chained together as an example in this article.
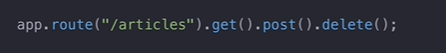
Refactoring routes code by chaining the routes.

Route Chaining in Express JS Example Code
const express = require("express");
const bodyParser = require("body-parser");
const ejs = require("ejs");
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
const { response } = require("express");
const app = express();
app.set('view engine', 'ejs');
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({
extended: true
}));
app.use(express.static("public"));
const uri = "mongodb://localhost:27017/wikiDB"
mongoose.connect(uri, {useNewUrlParser: true, useUnifiedTopology: true});
const articleSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
title:String,
content: String
});
const Article = mongoose.model("Article", articleSchema);
app.route("/articles").get(function(req, res){
Article.find(function(err, foundArticles){
if(!err){
res.send(foundArticles);
}else{
res.send(err);
}
});
})
.post(function(req,res){
const newArticle = new Article({
title: req.body.title,
content: req.body.content
});
newArticle.save(function(err){
if(!err){
res.send("Successfully added new article");
}else{
res.send(err);
}
});
})
.delete(function(req,res){
Article.deleteMany(function(err){
if(!err){
res.send("Successfully deleted all articles");
} else{
res.send(err);
}
});
});
app.listen(3000, function() {
console.log("Server started on port 3000");
});
